IoT based Smart Delivery Agricultural Systems
IoT based Smart Delivery Agricultural Systems
Bhumika Mohanty
GVN, The Global School, Bhopal
bmohanty6177@gmail.com
Introduction
The Internet of things (IoT) describes physical objects that are embedded with sensors, processing ability, software, and other technologies, and that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. Internet of things (IoT) device is a physical object that connects to the internet. IoT applications run on IoT devices and can be created to be specific to almost every application for industry, agriculture, healthcare, and smart. IoT applications use artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine learning approaches to improve intelligence to their devices.
In IoT based smart agriculture, a system is formed to monitor the farmland with the help of sensors, which senses components like temperature, light, humidity, soil moisture, chemical application, and health of livestock, etc. and automate the irrigation system that allows farmers to monitor their field from anywhere through IoT Analytics Platform. On farms, IoT allows devices across a farm to measure all kinds of data remotely and provide this information to the farmer in real-time. Farmers can get access to real-time data without human intervention. IoT devices can gather information like soil moisture. The growth of IoT devices in agriculture is about 20% annually and is expected to grow exponentially in the future.
Agricultural operations have seen numerous technological transformations in recent times and have become more industry-oriented and technology-driven. By using smart gadgets, and devices, farmers have achieved better control over various processes of raising field crops and livestock, and thus, made agricultural operations more predictable than before and improved their efficiency. The growing demand for agricultural products by consumers has contributed immensely to the increased popularity and proliferation of smart agricultural technologies in India and worldwide. In recent years, the share for IoT has been improved significantly in agriculture.
IoT Agriculture: The scope
IoT sensors are capable of providing the farming community with information that helps in improving crop yields, aiding various field operations such as pest and disease infestation, soil health and nutrition, machine operations, water management, crop monitoring and also various weather parameters like temperature, and humidity, etc. These parameters are invaluable to crop production and provide precise data, which are used to improve farm operations over a period of time (Fig. 1).
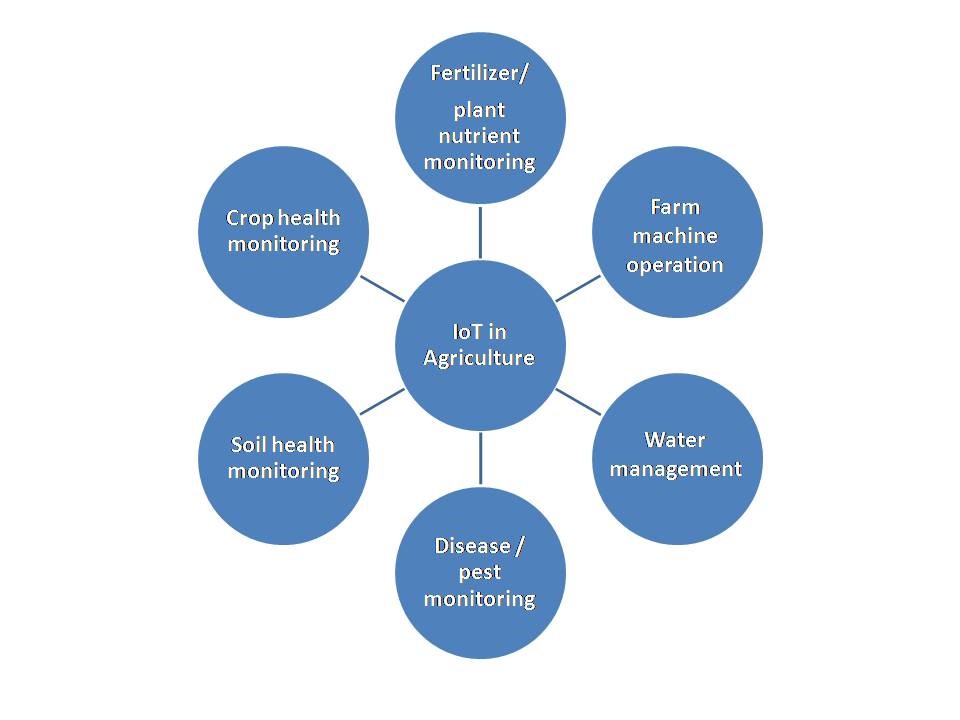
Benefits of IoT in agriculture
There are several benefits visualized in agriculture. A few are presented in fig. 2 and described below.
- Farmers can get access to collected data in real-time and without human intervention.
- Due to the evolution of technology, the size and shape of sensors are getting smaller and more sophisticated, while in parallel the general cost of IoT devices is getting lower.
Elements of IoT
The IoT systems represent the integration of four distinct components: sensors/devices, connectivity, data processing, and a user interface (Fig. 3).
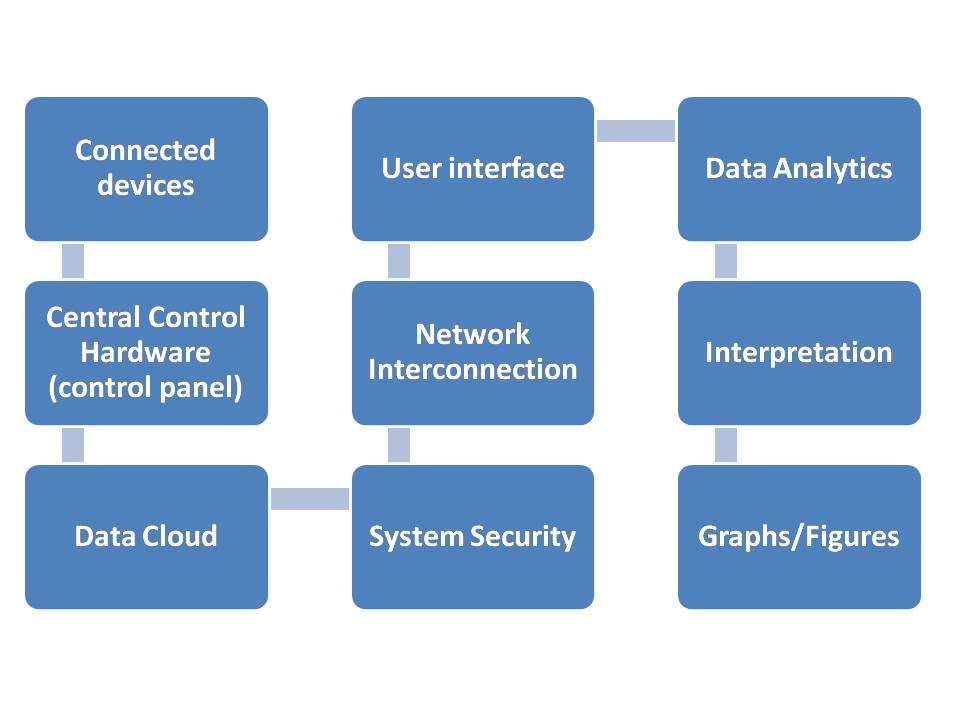
IoT technology used in agriculture
- Automation of Greenhouse: The IoT sensors provide accurate information on a real-time basis about temperature, relative humidity, lighting, humidity and soil condition in the greenhouse.
- Weather conditions and soil quality monitoring: The most popular smart gadgets in agriculture are automatic weather stations, comprising various sensors. The weather stations collect data from the sensors across the field and send them to the cloud. The measurements thus help to map the weather conditions, crop planning and help in precision farming. In addition to providing environmental information, weather stations adjust the environmental conditions automatically to match the given set of parameters. This is very much important and applicable to the greenhouse systems where the more precise application of water and nutrients are required to control crop growth and yield.
- Crop management: Crop management devices are other important IoT products in agriculture and are part of precision farming for crop management. These devices are placed in the field like automatic weather stations to supply observations specific to crop management starting from temperature, leaf water potential, crop health and other important information related to yield.
- Precision farming: Sensors provide information to farmers from a range of metrics starting from soil condition, lighting, humidity, temperature, CO2 concentration, and pest and disease infections. This helps farmers to take appropriate decisions on optimal amounts of water and fertilizers applications to fields as and when required, and the right amount of pesticides applied to crops when needed to reduce expenses and environmental pollution, health hazards, and raise better and healthier crops. This also helps in maintaining better biodiversity in the farmers’ fields and enhances product quality because of better production processes. Greater crop quality is maintained through this automation process.
- Livestock health monitoring: The IoT sensors are attached to the livestock /cattle in a farm to monitor their health and performance. Tracking livestock and monitoring their health, physical location and well-being, are important in maintaining a good stock for better yield compared to conventional farming.
- Crop’s harvest: IoT-based farming gives a predictive analysis about the amount of crops to be harvested, the quantity of grain yield to be obtained and thus, losses are controlled. Predictive analytics and precision agriculture go hand in hand. Smart sensors and IoT and technology are the sources of supply for a high quality and relevant data in real-time. The data analytics benefits farmers to come up with very important predictions like the time of crop harvest, the spread of diseases and pest infestations, yield, etc. Data analytics make farming more profitable and less risk-prone, more predictable and manageable at field scale. These tools manage the cost of production and reduce waste due to increased control over the harvested amount of crops. Thus, these mitigate the risk of losing crop yield and outputs from animals.
- Increased efficiency of farming: Multiple farm management processes like fertilization, water application, and pest and disease control are used simultaneously in IoT. Farm productivity is properly managed through IoT systems. This depends on the number of IoT devices, sensors installed on the farm and the powerful dashboard with good analytical abilities and in-built reporting features.
Conclusion
Through IoT, the farmers and the companies enjoy profits in the form of better productivity of field crops and safety to the farmers and other workers. Application of fertilizer nutrients, water, herbicides, insecticides, fungicides and pesticides are minimized. This process reduces the runoff loss of harmful chemicals to ground and surface water like rivers and lakes. This results in less stress on the ecosystem. IoT has a positive impact on the healthcare systems by reducing the healthcare costs on the government and improving the quality of life, and reduced carbon footprints. IoT may be served as a climate-resilient technology or system in agriculture.
